Learn Something New
Master your knowledge around debt repayment and make smarter financial decisions in the future.
Earn Perk Points
Each course completed earns you Perk Points. These points give you entries to win free $$$! Earn a shot to win every week!
Win Free Cash
Each week we raffle off free $$$ ($100 minimum). You learn, you pay off your debt, and you win extra cash toward your goals!

Simple Interest
Simple interest is just what its name suggests: simple. Simple interest charges are calculated on a daily basis and then added to your original loan amount (principal). Unlike compound interest, you will not be charged interest on top of the interest that accumulates between the time of your scheduled payment dates.
Simple interest is easily calculated A = P(1 + rt)
A = Total accrued amount (Principal Balance + Interest)
P = Principal Amount
I = Interest Amount
r = Rate of Interest per year in decimal (rate = r/100)
r = Rate of Interest per year as a percent; (rate = r * 100)
t = Time Period involved in months or years
Pro Tip: Most loans provided by lenders and the federal government are simple interest. Always read any finance agreement when taking out loans as the agreement will explain how interest is charged.

Compound Interest
Compound interest is interest earned on unpaid interest. A bit of a head-scratcher, right? Some refer to it simply as “interest on interest.” Like we’ve learned, you pay interest on borrowed money. With compounding interest, when you don't pay the accrued interest, more interest gets added to the accrued interest. For example, you take out a loan of $10,000 with an annual compounding interest of 10%. At the end of year one, that loan will cost $11,000. The next year, that 10% interest rate will be added to the $11,000 rather than the initial $10,000 you took out. For short loan terms, this isn’t so bad. But the longer the loan term, the bigger that principal will grow.
Tip: Although a simple interest loan does not charge interest on top of interest fees between pay periods, any unpaid interest due to forbearance or pauses in payments will capitalize. This means the unpaid interest will now be added to the principle, and these fees will be charged interest if left unpaid.

Add-On Interest
Add-on interest is a type of interest that gets calculated at the start of a loan. The lender calculates the interest that would accrue over the loan term and adds it to the principal, so the original loan amount you receive includes interest. Although these loans are not as common, lenders like this type of interest. Even if you pay your loan off early, they still get the full amount of interest.

Why should I know these terms?
We all work very hard for every dollar we earn. If you don't understand how interest charges accumulate, you can end up giving yourself a pay cut. After understanding how taxes, monthly expenses, and fees like interest charges cost, the average American only gets to keep a fraction of what they earn to save. This makes it more difficult to save for the future you dream of, so make sure to understand the best ways to borrow money!

What is debt consolidation?
Debt repayment can become overwhelming when you have multiple loans. Different loans with unique interest rates and varying monthly payments and terms can be tough to keep track of. What if you could roll all your debts into one debt with one payment? That’s debt consolidation. Through consolidation you can reorganize your debt and pay it down faster with a single monthly payment. Along with the simplification of your debt, you can also secure a lower interest rate. As you might have realized by now, the lower the interest rate, the better!

What are some ways to consolidate?
There are a few different ways to go about consolidating your debt. It depends on the type of loans you have, your credit score, and your financial situation. The following are common ways to consolidate.
Balance-transfer credit card: This is a type of credit card that you can transfer all your debts on to. If you have credit cards with high interest rates, this is a good option that can leave you with a lower interest rate. You will likely need good or excellent credit (690 or higher) to qualify.
Debt consolidation loan: The basic type of consolidation. Roll your debts into one single debt with one monthly payment. You can qualify for this type of loan if you have bad or fair credit (689 or below). Borrowers with higher scores will likely qualify for the lowest rates.
Student debt consolidation: This is consolidation for student loan borrowers. This is a good option for borrowers who have multiple federal student loans. The results give you one loan to make payments on rather than multiple payments and loans to keep track of. It's important to note that only federal loans are eligible for consolidation without the need of a credit check, but you won't necessarily get a better interest rate. Rates will normally be an average of all of your loans combined unless you refinance. We'll go over refinancing in the next section.

Is it right for me?
If you are looking to simplify and reorganize multiple loans, consolidation could be for you. A lower interest rate and improved monthly payments make it more efficient to pay down your debt as well. But it’s important to note that debt consolidation isn’t perfect for everyone. If your credit score is not great, you won't qualify for a lower interest rate. You might even end up with a higher one. There can also be fees such as loan origination fees, balance transfer fees, closing costs, or annual fees. Double-check to make sure you are aware of any penalties or fees ahead of time!

What is refinancing?
Refinancing is the process of taking out a new loan to pay off your current loan. Debt consolidation is all about reorganizing your loans, and refinancing is about getting a loan with better terms. By refinancing, a borrower can receive a lower interest rate, lower monthly payments, and/or a different loan term. Our financial situations change over time. With refinancing, you can check in to see if there are more favorable terms for your loan.

Why do I refinance?
Auto loans, mortgages, student loans, and credit card debt can be refinanced. Credit score is a major factor in getting the best terms. Make sure you sort out any credit issues so you can qualify for the lowest interest rates. This is your chance to get better terms that can improve your financial situation, so be sure to check out multiple lenders when looking to refinance.
Tip: Many lenders can prequalify your expected interest and loan term without making a hard credit pull. If available, this won't impact your credit score when shopping for the best rate.

Is it right for me?
Refinancing can be a great option for anyone looking for better terms on their loan. Be aware that refinancing isn't for everyone and can come with strings attached. Depending on the lender, there can be fees and prepayment penalties. You can extend or shorten the term of the loan, but remember that could also mean paying more in interest. Factor in everything and see if it best fits your situation.

What are these snow-based methods?
Don't worry, no snow is involved! In the previous sections we covered consolidation and refinancing, two tactics to help you repay your debts. But what if you'd rather not go through the process of getting another loan, or you have credit troubles and can't? Debt avalanche and debt snowball are two strategies that help you accelerate payments and get you out of debt sooner ... on your own! These methods will help you build a plan and focus your repayment one loan at a time ... and help you save more!

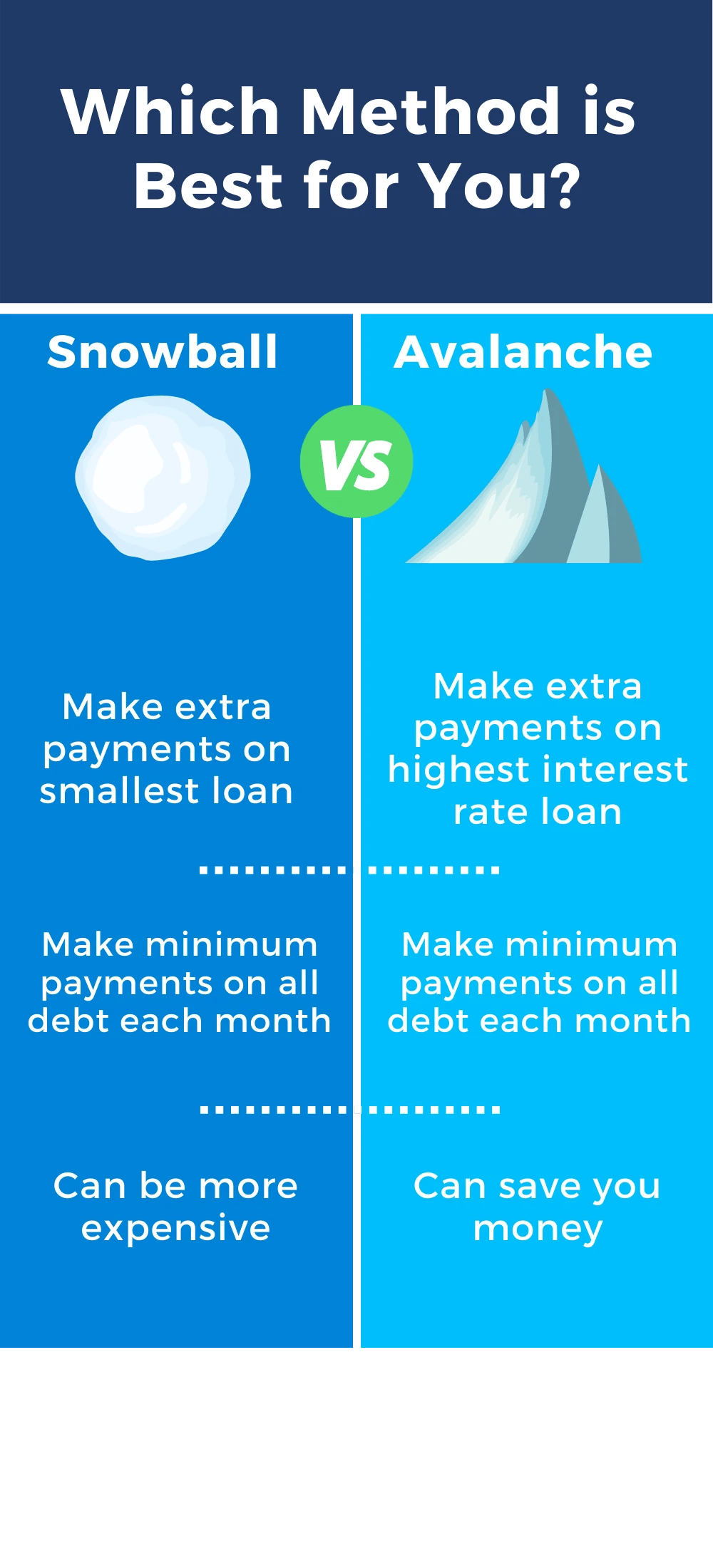
Avalanche Method
The debt avalanche method aims to eliminate your highest-interest debts first. To follow this method, you make minimum payments on all your debts each month. Then, with any spare money, make extra payments on the highest-interest debt. Using this method can save you a lot on interest, as you are targeting those high interest rates first. The avalanche method is best for saving money and time, but it's not the easiest. You must be disciplined, as you won't see immediate results like you would with the snowball method. Be aggressive with payments, and you will see great results in the end!
Follow this formula: Interest Rate x Current Principal / 365. For example, say I have an interest rate of 5.05% and a current loan balance of $25,000. Do the math: 0.0505 x 25,000 / 365 = 3.45. This means that a total of $3.45 will be added to your loan EACH DAY, making it $25,003.45 after one day. That's a cup of that fancy coffee you always like to get. It seems small now, but over time, that can turn into thousands of dollars if you don't make regular payments!

Snowball Method
The debt snowball method aims to eliminate your smallest debts first. To follow this method, make minimum payments on all your debts each month. Then make extra payments on your smallest debt. Once you finish paying your smallest debt, you do the same thing to the next smallest one. With the snowball method, it's easier to get excited about paying off your debt. You see the results faster than you would using the avalanche method. The biggest downside of the debt snowball is it can be a more expensive method. More interest will add up and end up costing you more in the long run. Although this repayment method can cost more, it has been proven to help people pay off debt more successfully. It's all about small wins!

What is defaulting?
When you take out a loan, you have all the intentions to pay it back. But as we all know ... life happens. Whether it's unexpected bills or sudden job changes, things happen that make it tough to pay debt. A loan will enter default when you fail to make payments for a certain period of time. Each loan type has a unique amount of days it takes to enter default after the last payment. Check out our list below to see those time frames!
Note: The days below are not the case for every loan, just what is seen typically.

What happens when you default?
Defaulting is a worst-case scenario, so it's no surprise that it comes with some consequences. It's a red flag to future lenders and financial institutions. Defaulting will be a major hit on your credit score, since your score is based heavily on payment history. With default come more fees. Late payment fees and penalties can be added onto your debt. It will also be difficult to get future loans.
If you default on a secured loan, the collateral you offered most likely will be reclaimed. Mortgages are secured loans, meaning your home can be foreclosed on to pay off your debt. Unsecured loans like student loans and credit cards have no collateral, so the damage is done mostly to your credit. In some very bad cases, the government could step in and garnish wages or withhold tax refunds. This applies more so for defaulting on federal student loans.

Can I avoid it?
We have established that defaulting on a loan is scary. Sadly, once you default, there isn't much you can do. But what you can do is avoid it! When you feel like payments are becoming a struggle, reach out to your lender.
Communication is key here, and by reaching out, you show the lender that you are making an effort. A plan can be reached to make payments doable. There is a period between missing a loan payment and having the loan default. This period is known as delinquency. It gives you time to avoid default and to contact your loan servicer or make up missed payments. Federal student loans luckily have other options to explore like deferment, forbearance, and income-based payments. The important thing is to take action as soon as payments feel difficult!

Changed in the News

7 Tips to Prepare Yourself Before Student Loan Repayment
Student loan debt doesn't have to be a mystery. Learn about loan repayment before you get there.

Student Loan Repayment: A Family Affair
Changed has launched the Family and Loved Ones feature so those who want to help most, can.
Read more
Changed on ABC's Shark Tank
Changed, an app that rounds up the spare change from your everyday purchases to help you pay off your student loans sooner and for less in interest costs, will appear on ABC's popular Emmy-Award-winning reality show Shark Tank Jan. 28 at 8 p.m. CT.
Read more
Changed Founders "Embrace the Broom"
Startup founders who landed a deal with Mark Cuban on 'Shark Tank' used a 100-year-old piece of advice to build their company from the ground up.
Read more
Changed Featured in Money Magazine
Three years ago, Dan Stelmach was stuck in a sales job he didn’t like, trapped by the $850 student debt payments he had to make each month.
Read more
Simple Tips to Knock Out Student Loans Debt
Discover simple steps you can start taking today to pay off your debt faster.
Read more
